Introduction
Gap analysis is a crucial technique within the TOGAF (The Open Group Architecture Framework) Architecture Development Method (ADM). It helps organizations identify discrepancies between their current (baseline) and desired (target) architectures. Visual Paradigm provides robust support for conducting gap analysis, facilitating effective enterprise architecture development. This guide will walk you through the process of performing gap analysis using Visual Paradigm within the TOGAF ADM framework.

Table of Contents
- Understanding Gap Analysis in TOGAF
- Steps to Conduct Gap Analysis Using Visual Paradigm
- Define the Scope
- Establish the Current State
- Identify the Desired Future State
- Analyze Gaps
- Prioritize Gaps
- Develop a Transition Roadmap
- Key Features of Visual Paradigm for Gap Analysis
- Examples of Gap Analysis
- Resources for Further Learning
1. Understanding Gap Analysis in TOGAF
Gap analysis in TOGAF is a systematic approach to identify and address the differences between the current and target architectures. It involves assessing various architectural domains, such as Business, Data, Application, and Technology Architecture, to ensure they align with organizational goals and objectives.
2. Steps to Conduct Gap Analysis Using Visual Paradigm
Define the Scope
- Identify Architectural Domains: Determine which architectural domains need assessment. This could include Business Architecture, Data Architecture, Application Architecture, and Technology Architecture.
- Align with Business Goals: Ensure that the scope aligns with the strategic objectives of the organization.
Establish the Current State
- Gather Data: Collect information through stakeholder interviews, reviews of existing architectural artifacts, and analysis of current business processes.
- Document Current Architecture: Use Visual Paradigm to create detailed diagrams representing the current architecture. Utilize tools like BPMN for modeling business processes.
Identify the Desired Future State
- Define Vision: Create high-level vision documents outlining what the future state should look like.
- Detailed Process Models: Use Visual Paradigm’s modeling tools to develop detailed process models that reflect the desired future state.
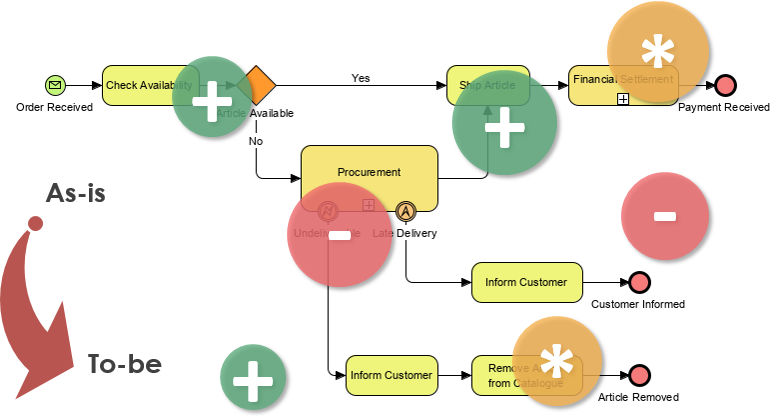
Analyze Gaps
- Compare Architectures: Compare the baseline architecture against the target architecture to identify gaps. These gaps may include missing capabilities, processes, or technologies.
- Visualize Discrepancies: Use Visual Paradigm’s gap analysis tools to visualize these discrepancies effectively.
Prioritize Gaps
- Impact Analysis: Prioritize identified gaps based on their impact on organizational goals and objectives.
- Resource Allocation: Focus resources on addressing the most critical gaps first.
Develop a Transition Roadmap
- Create a Migration Plan: Develop a detailed plan to bridge identified gaps. Include timelines, resources required, and responsible parties.
- Simulate Solutions: Use Visual Paradigm’s simulation capabilities to evaluate potential solutions and their impacts on identified gaps.
3. Key Features of Visual Paradigm for Gap Analysis
- BPMN Support: Full support for BPMN to model business processes accurately.
- Drag-and-Drop Interface: User-friendly interface for easy diagram creation.
- Simulation Capabilities: Simulate business processes to evaluate potential solutions.
- Collaboration Tools: Support for team collaboration, enabling multiple stakeholders to contribute.
- Reporting Features: Generate reports summarizing findings from the gap analysis.
4. Examples of Gap Analysis
Example 1: Business Process Improvement
- Current State: Inefficient manual processes leading to delays.
- Future State: Automated processes reducing delays and improving efficiency.
- Gap Analysis: Identify manual steps that can be automated.
- Transition Roadmap: Implement automation tools and train staff.
Example 2: Technology Upgrade
- Current State: Outdated technology infrastructure.
- Future State: Modern, scalable technology infrastructure.
- Gap Analysis: Identify outdated technologies and their replacements.
- Transition Roadmap: Phase out old technologies and implement new ones.
5. Resources for Further Learning
-
Visual Paradigm Guides:
-
TOGAF Documentation:
-
Additional Resources:
Conclusion
Using Visual Paradigm for gap analysis within the TOGAF ADM framework allows organizations to systematically identify and address discrepancies between their current and desired architectures. By following a structured approach, organizations can enhance their architectural capabilities and align them with strategic business objectives effectively. This technique supports both process improvement and strategic planning for future developments within an organization’s architecture landscape.













